Author: Sebastian Westerhold
DSP Diode Clipping Algorithm for Overdrive and Distortion Effects
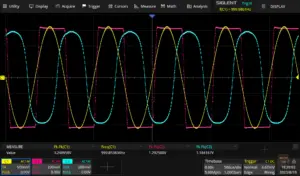
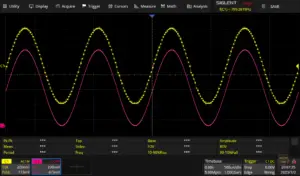
This article shows how to approximate the behaviour of a regular diode in a mathematical equation and how to subsequently implement the behaviour in software. The DSP algorithm can be modified to implement different topologies, such as single diode clipping, dual diode symmetrical soft clipping or asymmetrical clipping.
Critical length of a PCB trace and when to treat it as a transmission line

Ideally, the impedance of PCB traces should be matched to the load and source impedances. This becomes especially important in high-frequency and high-speed digital PCB designs. Various rules of thumb are available to determine the critical length at which a PCB trace should be treated as a transmission line. Below this critical length, an impedance mismatch can safely be ignored. Or can it?
Etching PCBs using hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide

Choosing the right etchant for home made PCBs could be a science on its own. Some people prefer ferric chloride, some advocate for sodium persulfate and I personally prefer hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide. This article shows how to use a mixture of hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide in a safe and controllable manner.
Universal Clock Translator using Renesas VersaClock 6E Devices

Due to the popularity of the QO-100 geostationary amateur radio communication satellite, precision GPS reference frequency sources (GPSDO) are becoming more and more common in home labs. The desire to derive different, fixed frequency signals from a GPSDO has similarly been increasing as different devices requiere different reference clocks with different frequencies. Therefore, this article is taking a closer look at the VersaClock 6E devices from Renesas.
Program uBlox GPS-module timepulse frequency (dynamically) with an Arduino
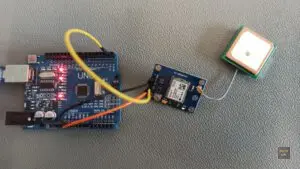
The uBlox GPS-modules are capable of providing various reference clock signals through the TIMEPULSE pin. By default, this pin outputs a 1 pulse-per-second (PPS) signal. For an upcoming project, a GPS disciplined oscillator (GPSDO), this output had to be adjusted to 100 kHz. Instead of using the manufactuer’s software, u-center, this task is supposed to be accomplished using an Arduino. This article shows how to (dynamically) adjust the TIMEPULSE reference signal using an Arduino.